POLYSACCHARIDES
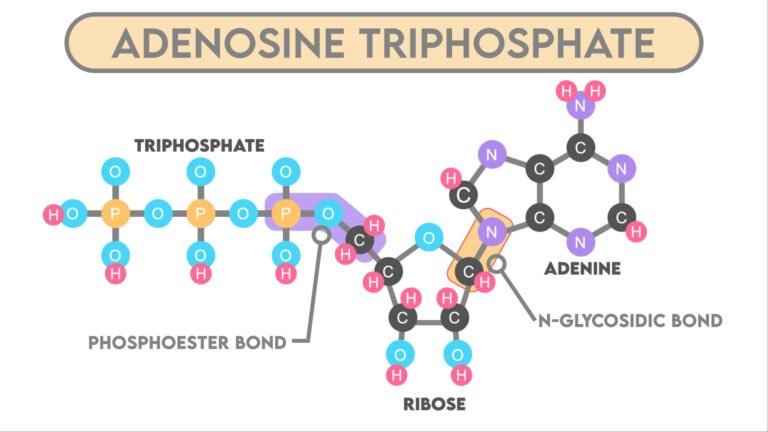
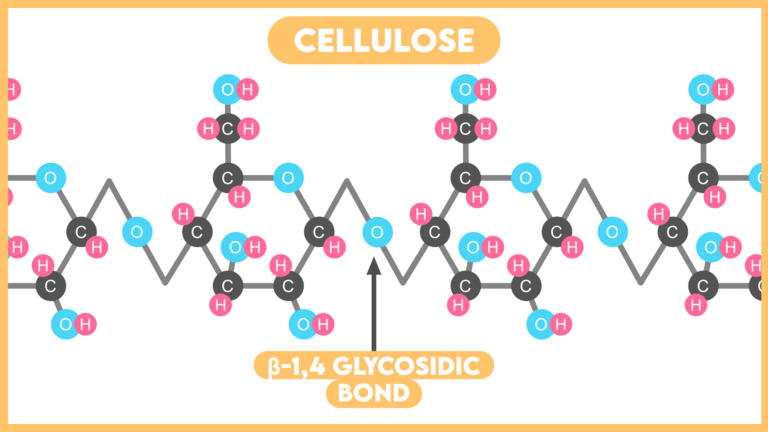
IMPORTANT POINTS Polysaccharides are the polymers of Monosaccharides having more than 10 units. Polysaccharides are Biomacromolecules. Polysaccharides even though classified as saccharides are not sweet in taste. During formation of a Polysaccharide, new monosaccharides residues are added at the non-reducing end of the chain CLASSIFICATION OF POLYSACCHARIDES On the basis