IMPORTANT POINTS
- Study of Pollen is called Palynology.
- Typical shape- Spherical
- Size- 25-50 um (in diameter)
- Pollen grain represents the male gametophyte i.e. it carries the male gametes to the female reproductive parts in Gymnosperms and Angiosperms.
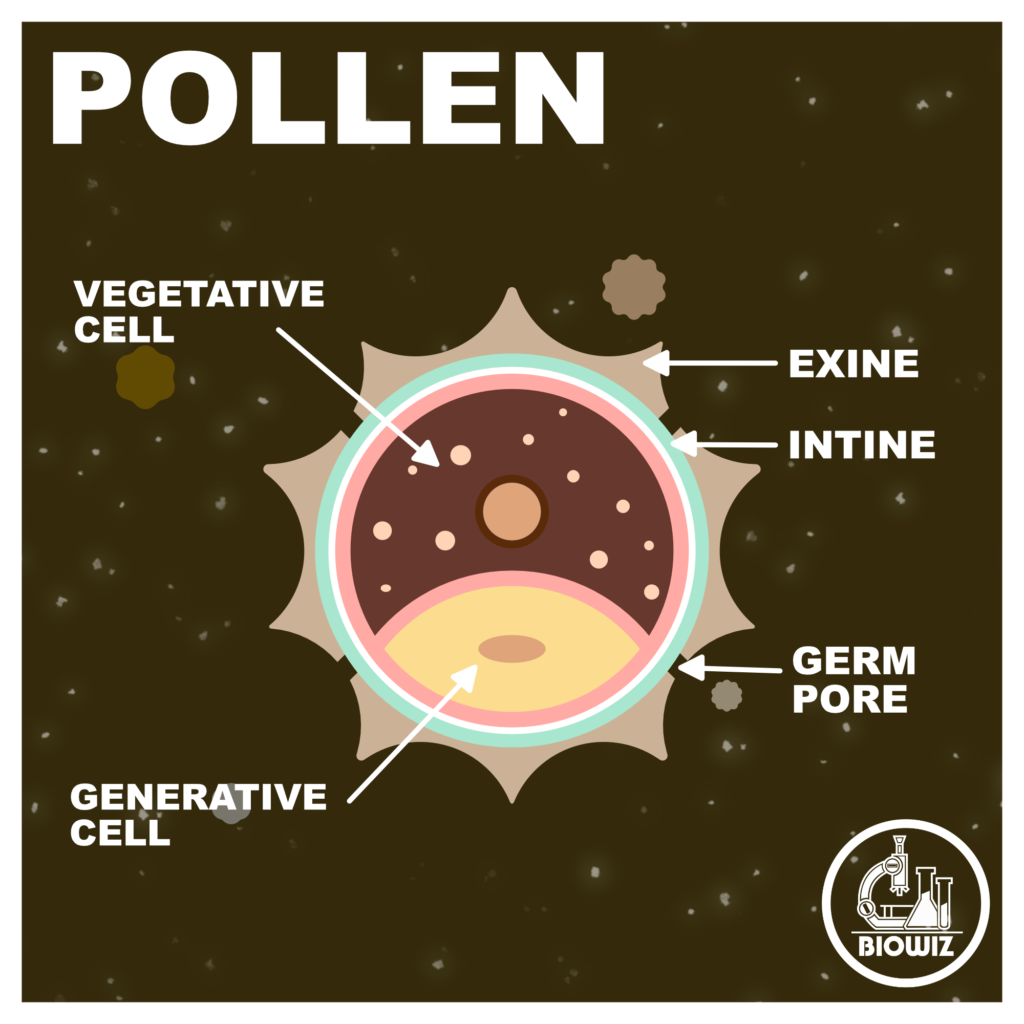
STRUCTURE OF POLLEN
POLLEN WALL
Pollen has a prominent two-layered wall i.e. Exine and Intine.
EXINE
- Outermost protective layer of the pollen
- Hard and thick layer
- Discontinuous layer as exine has prominent apertures called Germ Pores
- Exine exhibits fascinating array of patterns and designs
- Made up of Sporopollenin (most resistant organic material known)
INTINE
- Thin and elastic layer
- Continuous layer
- Made up of cellulose and pectin
CELLS
A mature pollen consist of two cells i.e. Vegetative cell and Generative cell
VEGETATIVE CELL
- Large in size
- Nucleus is large and irregularly shaped
- Contains abundant food reserve
- Fn- Helps in development of pollen tube
GENERATIVE CELL
- Small in size
- Floats in the cytoplasm of vegetative cell
- Nucleus is Spindle shaped
- Contains dense cytoplasm
- Fn- Divides by mitosis to form two non-motile male gametes.
ADVANTAGES OF POLLEN
TO PLANTS
- Carries male gametes to the female sex organ for fertilisation.
- Enabled the higher plants (Gymnosperms and Angiosperms) to grow in a wide range of terrestrial habitat as pollen eliminated the dependence on water for fertilisation.
TO HUMANS
- Pollen are rich in nutrients and are used as food supplements.
- Pollen consumption increases the performances of athletes and race horses.
- Pollen can be preserved using liquid Nitrogen for future use (Cryopreservation)
DISADVANTAGES OF POLLEN
- Pollen are small in size so can be inhaled during breathing.
- Pollen of many species causes severe allergies and bronchial afflictions in some people.