
MANGO
Mango is a type of Drupe fruit having a single seed and stony endocarp. The edible part is the juicy mesocarp.

Mango is a type of Drupe fruit having a single seed and stony endocarp. The edible part is the juicy mesocarp.

Maize, or Zea mays, is a monocot plant from the Poaceae family, producing unisexual flowers on the same plant, and is notable for its unique caryopsis fruit where the seed coat and fruit wall are fused.

Pteridophytes, also known as vascular amphibians, exhibit a diplo-haplontic life cycle, where the dominant sporophyte is well-differentiated with true roots, stems, and leaves, while the reduced gametophyte is heart-shaped and photosynthetic.

The life cycle of bryophytes involves alternation of generations between the dominant gametophyte and the sporophyte. The gametophyte produces gametes that unite to form a sporophyte, which generates spores. These spores develop into new gametophytes, ensuring the perpetuation and propagation of bryophyte species through this cyclical process.

Leaves come in various types, each uniquely adapted to their environment. Simple leaves have a single blade, while compound leaves consist of multiple leaflets. Their shapes vary from broad to needle-like, optimizing photosynthesis and water conservation. Understanding leaf types helps in identifying plants and their ecological roles.

The regulation of the lac operon in E. coli is a classic example of gene control. It involves an operon system where the presence or absence of lactose determines the transcription of genes responsible for lactose metabolism. The operon is activated by lactose and inhibited by glucose, ensuring efficient energy

Hydroponics is a method of growing plants without soil, using nutrient-rich water solutions. This innovative technique allows for precise control over plant nutrition, faster growth rates, and efficient use of space and resources. Ideal for urban farming, hydroponics supports sustainable agriculture and year-round crop production.
Gymnosperms are seed-producing plants with naked seeds, not enclosed by fruit. They include conifers like pine and cedar, thriving in diverse habitats. Key features: needle-like leaves, cones for reproduction, and adaptability to various climates.
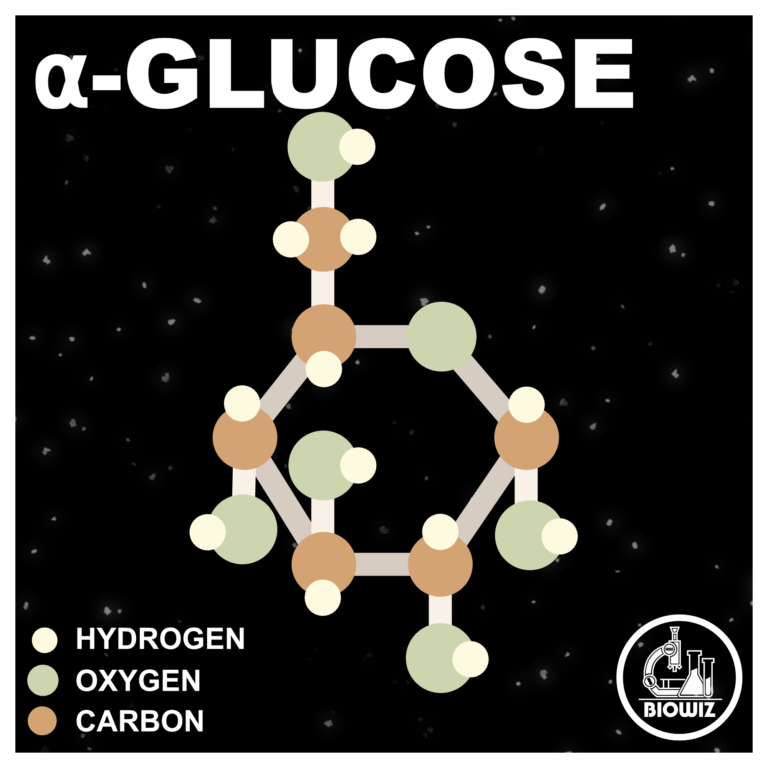
α-Glucose is a vital monosaccharide and a fundamental building block in biochemistry. Its unique ring structure allows it to form polysaccharides like starch and glycogen, essential for energy storage in plants and animals. Understanding α-glucose’s role helps elucidate complex biological processes and energy transformations