IMPORTANT POINTS
- Polysaccharides are the polymers of Monosaccharides having more than 10 units.
- Polysaccharides are Biomacromolecules.
- Polysaccharides even though classified as saccharides are not sweet in taste.
- During formation of a Polysaccharide, new monosaccharides residues are added at the non-reducing end of the chain
CLASSIFICATION OF POLYSACCHARIDES
- On the basis of type of Repeating Units
- HOMOPOLYSACCHARIDES
- HETEROPOLYSACCHARIDES
- On the basis of their Role
- STRUCTURAL POLYSACCHARIDES
- STORAGE POLYSACCHARIDES
1. STRUCTURAL POLYSACCHARIDES
- CELLULOSE
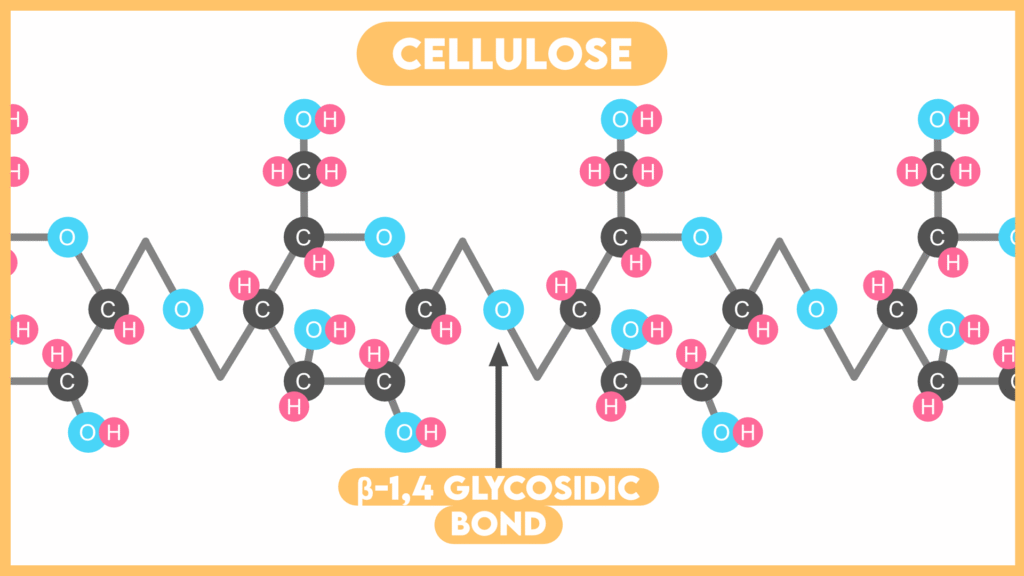
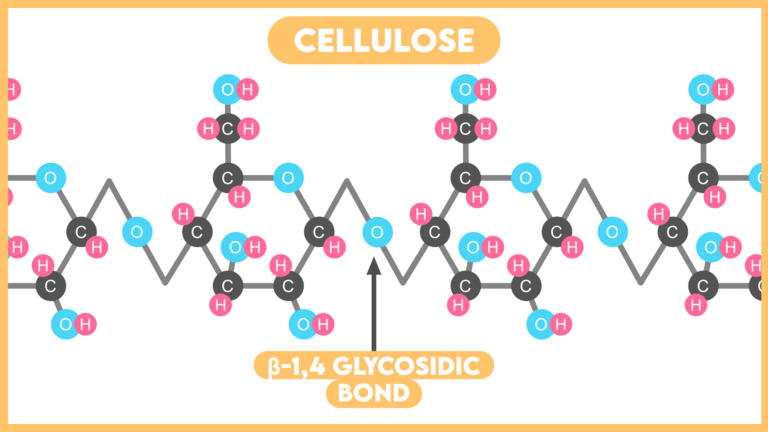
- Cellulose is a Homopolymer of β-glucose.
- Monosaccharide units of β-glucose are joined by β-(1,4) glycosidic bond.
- Cellulose is a linear straight chain molecule.
- Cellulose is the most abundant organic molecule on Earth.
- Found in the cell wall of plants and spores of some slime moulds.
- CHITIN
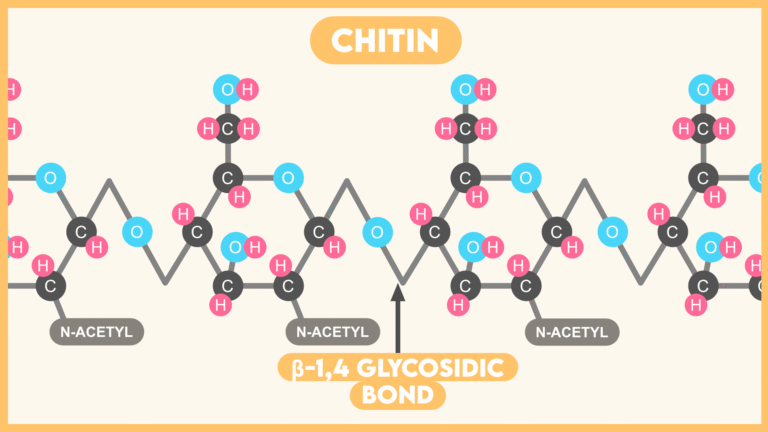
- Chitin is a Homopolymer of N-acetyl Glucosamine (NAG) which is an amino sugar having N-acetylated amino group.
- NAG units of Chitin are joined by β-(1,4) glycosidic bond.
- Chitin is also a linear straight chain molecule but can form helices in its secondary form.
- Chitin is the second most abundant organic matter present on Earth.
- Found in the cell wall of Fungi and Exoskeleton of Arthropods.
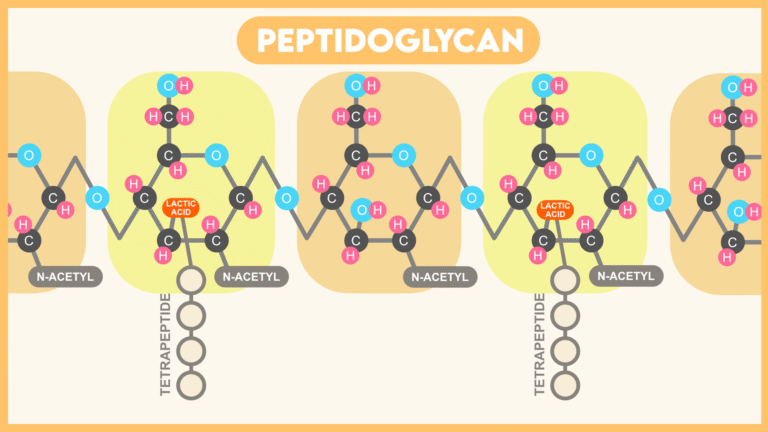
- PEPTIDOGLYCAN
- Chitin is a Heteropolymer of N-acetyl Glucosamine (NAG) and N-acetyl muramic acid (NAM) [Both NAG and NAM are amino sugars].
- NAG and NAM units of Peptidoglycan are joined by β-(1,4) glycosidic bond.
- Found in the cell wall of Eubacteria.
- OTHER STRUCTURAL POLYSACCHARIDES
- PECTINS
- HEMICELLULOSE
2. STORAGE POLYSACCHARIDES
- STARCH (AMYLUM)
- Starch is a Homopolymer of α-glucose units.
α-glucose units are joined by Glycosidic bonds.
- Reserve food in Plants and found as insoluble granules in the chloroplast.
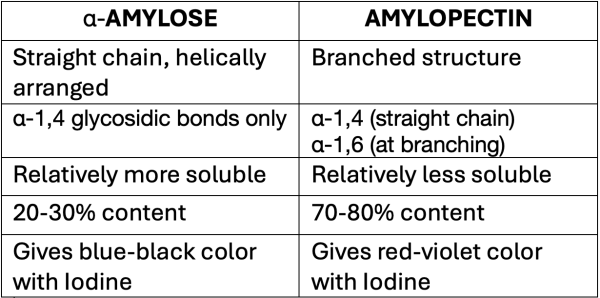
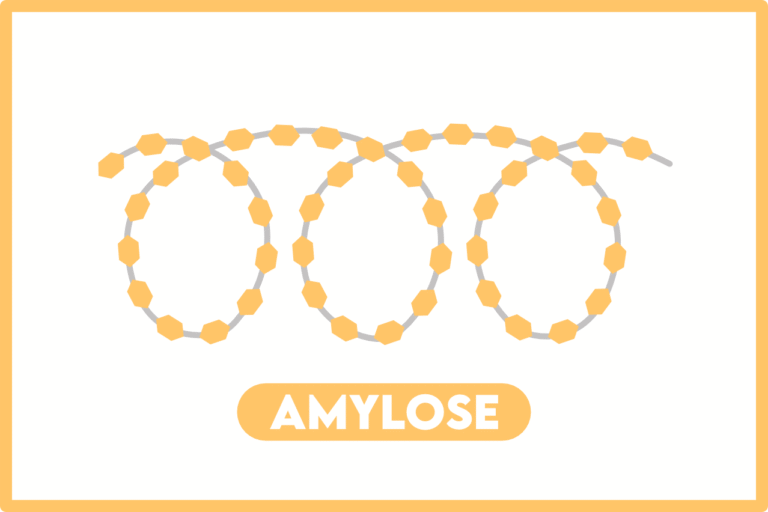
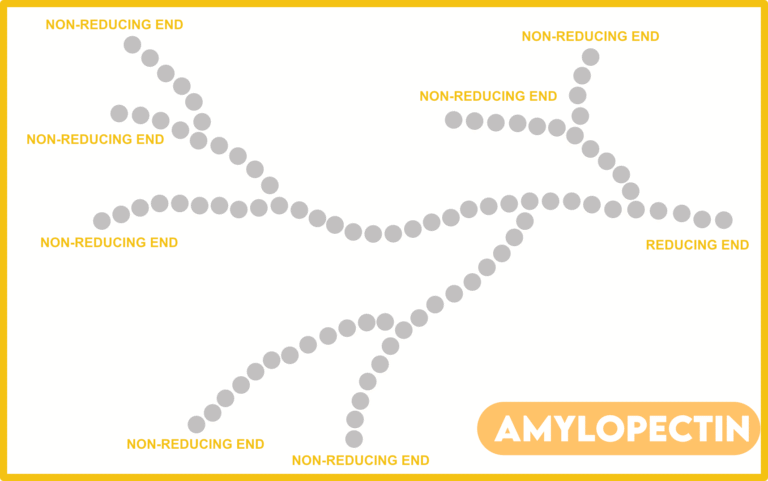
- Starch is made up of α-amylose and Amylopectin.
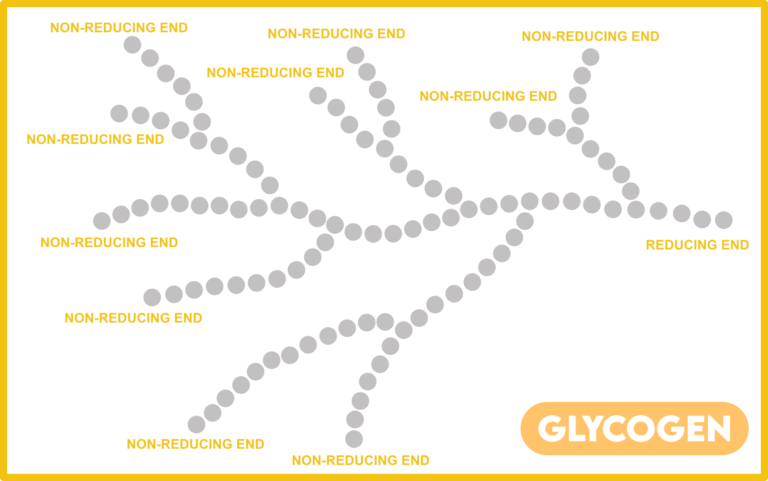
- GLYCOGEN
- Starch is a Homopolymer of α-glucose units.
- Glycogen is similar in structure as compared to amylopectin but is relatively more branched.
- Glycogen is the reserve food in most bacteria, fungi and animals.
- Gives red color with Iodine.
- Number of non-reducing ends in a Glycogen molecule = No. of branch points + 1.
- Number of reducing ends = 1 (right side)
- INULIN
- Inulin is a Homopolymer of fructose units.
- Fructose units are joined by β-(2,1) glycosidic bond
- Stored in the roots of Dahlia and and related plants.
- Inulin is a water soluble polysaccharide.
- Inulin is not metabolized in the human body and hence used for kidney function test.