The process of reproduction in Fungi can occur simply through body parts (Vegetative) or by formation of haploid Asexual Spores (Asexual Reproduction) or by formation of gametes and sexual spores (Sexual Reproduction) .
The Fungi group produces several types of Asexual Spores. These spores are mostly haploid spores and are formed by mitotic divisions in the Haploid body of Fungi. Thus, these spores are also called Mitospores.
Examples of Asexual Spores of Fungi
- Zoospores
- Sporangiospores
- Conidiospores
- Oidia
- Chlamydospores
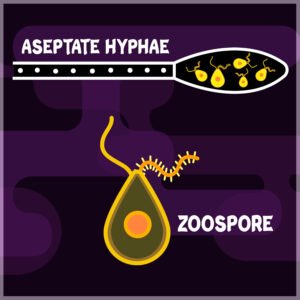
ZOOSPORES
- Endogenous spores
i.e. Formed inside a closed chamber called Zoosporangia - Motile spores
i.e. Flagella is present - Formed under favorable conditions
- Thin walled spores
- Present in members of the fungal class- Oomycetes (Phycomycetes)
SPORANGIOSPORES
- Endogenous spores
i.e. formed inside a closed chamber called Sporangia - Non-motile spores
i.e. Flagella is absent - Formed under favorable conditions
- Thin walled spores
- Present in the members of the fungal class- Zygomycetes (Phycomycetes)

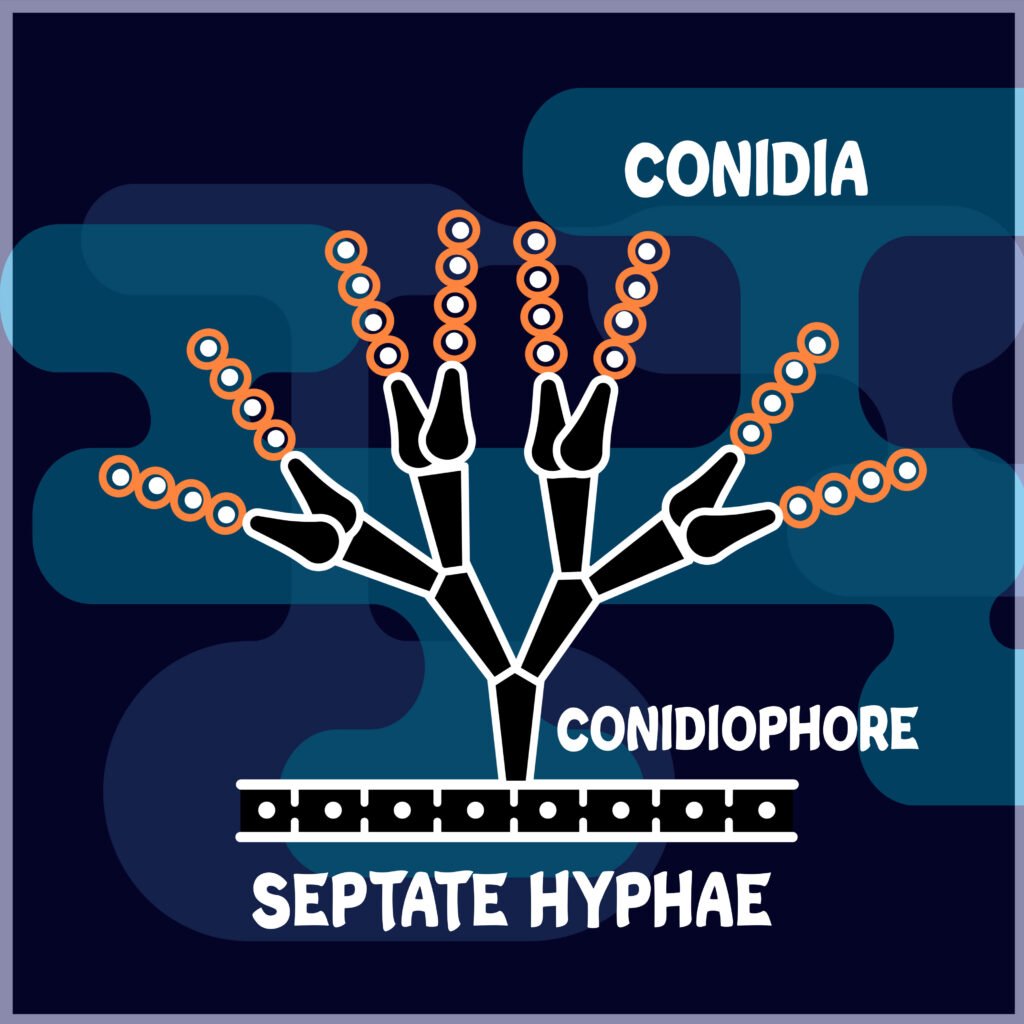
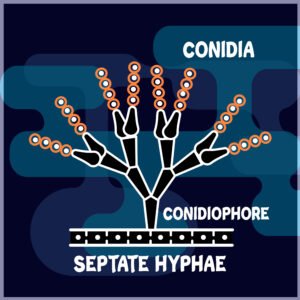
CONIDIOSPORES/ CONIDIA
- Exogenous spores
i.e. Formed outside the body - Non-motile spores
i.e. Flagella is absent - Formed under favorable conditions
- Thin walled spores
- Present in the members of the fungal class- Ascomycetes
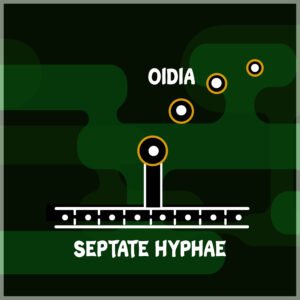
OIDIA
- Exogenous spores
- Non-motile spores
- Formed under highly favorable conditions (sugar solution)
- Thin walled spores
- Present in the members of the fungal class- Ascomycetes
CHLAMYDOSPORES
- Exogenous spores
- Non-motile
- Formed under unfavorable conditions
- Thick walled spores
- Present in the members of fungal classes- Ascomycetes

#asexual reproduction in fungi #biological classification, #class 11 biology #class 11 botany #types of asexual spores in fun