OSMOSIS
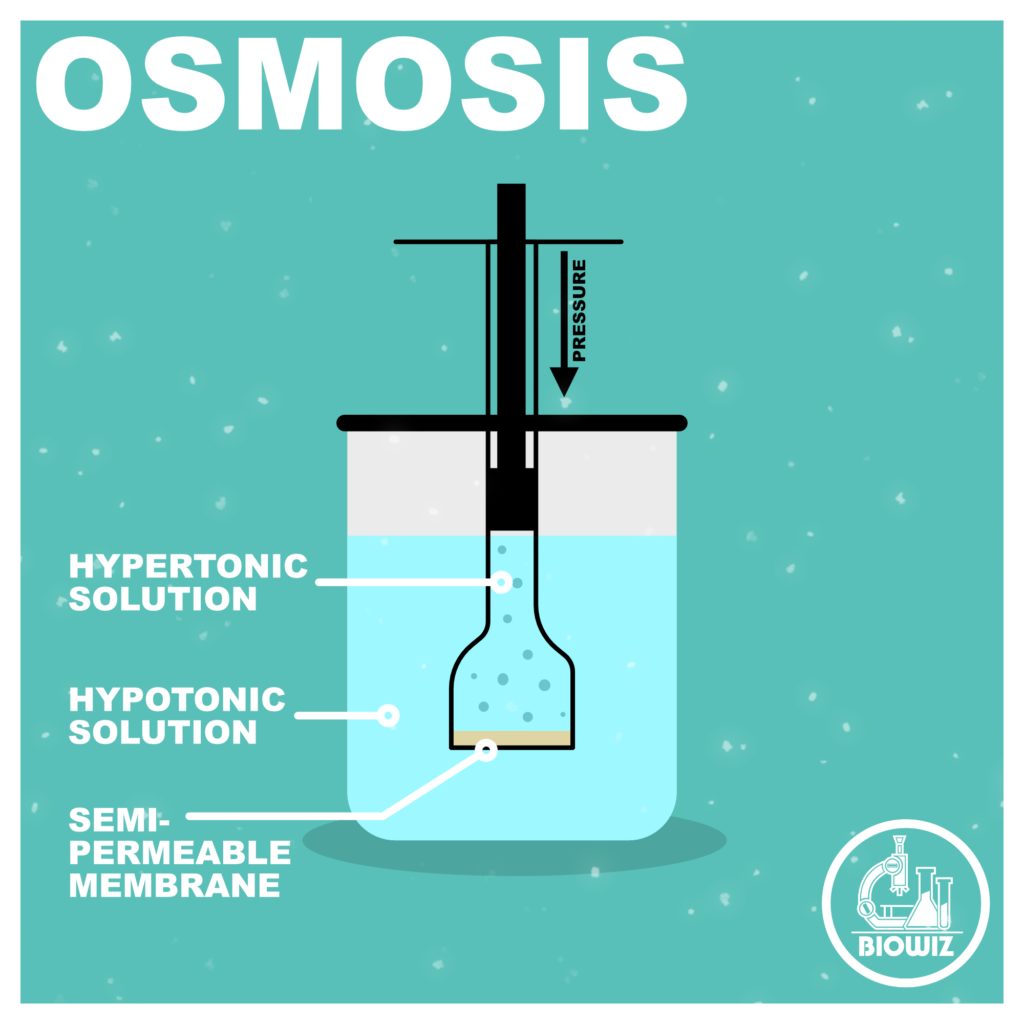
Osmosis is a special type of diffusion which involves movement of solvent (only) from region of its high concentration to region of its low concentration across a semi-permeable or selectively permeable membrane.
TYPES OF OSMOSIS
Osmosis can be divided into two types on the basis of direction of movement of solvent:
ENDOSMOSIS– When water enters the cell.
EXOSMOSIS– When water moves out of the cell.
Osmosis can be defined in several ways using different parameters:-
Osmosis is movement of solvent from :-
- region of its high concentration to region of its low concentration across a semi-permeable membrane.
- region of low solute concentration to region of high solute concentration across a semi-permeable membrane.
- dilute solution to concentrated solution across a semi-permeable membrane.
- Hypotonic solution to Hypertonic solution across a semi-permeable membrane.
- high Diffusion Pressure of solvent to low Diffusion Pressure of solvent across a semi-permeable membrane.
- low Osmotic Pressure to high Osmotic Pressure across a semi-permeable membrane.
- low Diffusion Pressure Deficit to high Diffusion Pressure Deficit across a semi-permeable membrane.
- high Solute Potential to low Solute Potential across a semi-permeable membrane.
- high Water Potential to low Water Potential across a semi-permeable membrane.
EXPLANATIONS OF THE TERMS USED
TYPES OF SOLUTION
- Hypotonic Solution- Solution having relatively less solute concentration is called Hypotonic solution
- Isotonic Solution- Solutions having exactly same solute concentration is called Isotonic solution
- Hypertonic Solution- Solution having relatively high solute concentration is called Hypertonic solution.
DIFFUSION PRESSURE
- The pressure exerted by the diffusing particles due to their kinetic energy is called Diffusion pressure.
- The maximum value of Diffusion Pressure is zero i.e. for a pure solvent.
- On adding some solute to the pure solvent, the solvent molecules starts to interact with the solutes. As a result, the free solvent molecules decreases resulting in decrease in the kinetic energy of diffusing solvent. This decrease in the kinetic energy is called Diffusion Pressure. Thus, for a solution value of DP will always be negative.
- When a solution (low DP) is separated from its pure solvent (high DP) through a semi-permeable membrane, the solution side has relatively less free solvent molecules than the pure solvent side. As a result, solvent will flow from pure solvent side to solution side to attain equilibrium. Thus, osmosis occurs from high DP to low DP.
OSMOTIC PRESSURE
- The pressure which develops in a solution when it is separated from its pure solvent by a semi-permeable membrane is called Osmotic Pressure (OP).
- The external pressure required to be applied in the solution side to stop the flow of solvent when it is separated from pure solvent by a semi-permeable membrane.
- OP is measured in atmosphere or bar units.
- For a pure solvent, the value of OP is zero. (Minimum value)
- For a solution, the value of OP is always positive.
- Osmotic pressure is directly proportional to the concentration of the solution.
- When a solution (high OP) is separated from its pure solvent (low OP) by a semi-permeable membrane, the solvent moves from pure solvent to solution side until equilibrium is reached. Thus, osmosis occurs from high OP to low OP.
TURGOR PRESSURE
- When a plant cell (or any cell with cell wall) is placed in a hypotonic solution, water will enter inside the cell (ENDOSMOSIS) due to its OP. As a result, the volume of the protoplast increases which exerts a pressure on the cell wall of the cell. This pressure is called Turgor Pressure (TP).
- A cell is said to be turgid when no more water can enter inside the cell. (OP=TP)
- When a plant cell (or any cell with cell wall) is placed in a hypertonic solution, the cell will start to loose water (first from cytoplasm then from vacuole) due to EXOSMOSIS. As a result, the volume of the protoplast decreases resulting in decrease in TP. When the protoplast exerts no pressure (TP=0) on the cell wall, the cell is called Flaccid cell.
- Further when a flaccid cell loose more water, the protoplast starts to detach from the cell wall. This is called Plasmolysis.
- The Turgor Pressure acts against the Osmotic Pressure.
DIFFUSION PRESSURE DEFICIT/ SUCTION PRESSURE
- The difference between the Diffusion Pressure of pure solvent and the Diffusion Pressure of the solution is called Diffusion Pressure Deficit.
- It is calculate by the formula: DPD= OP – TP
- For a pure solvent, DPD=0 (minimum value)
- For a solution, DPD is always positive.
- Osmosis occurs from low DPD to high DPD.
SOLUTE POTENTIAL
- When solute is added to pure solvent, the solvent particles starts to interact with the solute. As a result, the free energy of the solution decreases due to less free solvent molecules. This decrease in free energy of solvent on addition of solutes is called Solute Potential.
- For a pure solvent, Solute Potential is zero. (Maximum value)
- For a solution, the Solute Potential is always negative.
- The magnitude of Solute Potential is equal to Osmotic Pressure but with a negative sign. (Solute Potential= -Osmotic Potential)
- Osmosis occurs from high Solute Potential to low Solute Potential.
PRESSURE POTENTIAL
- The effect of pressure on the free energy of a solution is called Pressure potential
- For a solution at atmospheric pressure, the value of Pressure Potential is zero.
- The magnitude of Pressure Potential is equal to turgor Pressure with same sign.
WATER POTENTIAL
- The free energy of the solution depends on several factors including solute potential, Pressure potential etc. The effect of all these factors on the free energy is called Water Potential of the solution.
- For a pure solvent, Water Potential is zero. (Maximum value)
- For a solution, the Water Potential is always negative.
- The magnitude of Water Potential is equal to DPD but with a negative sign. (Solute Potential= -Osmotic Potential)
- Osmosis occurs from high Solute Potential to low Solute Potential.